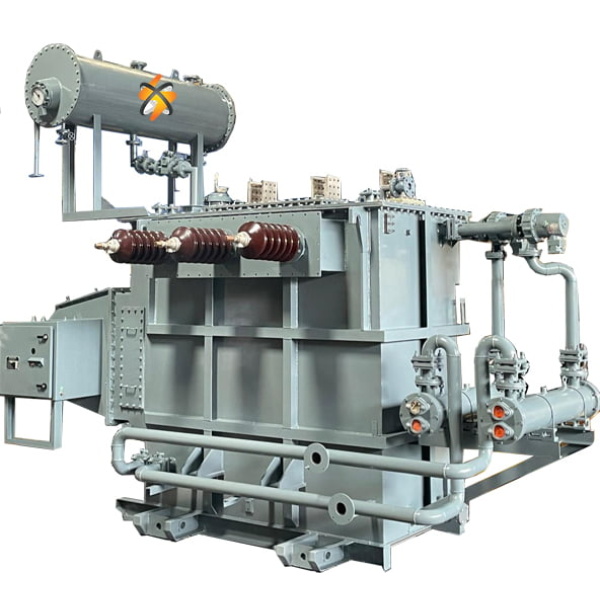
Description
Inverter duty transformers are specialized transformers designed to work efficiently with inverter-based power sources, such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) or other power conversion equipment like rectifiers and UPS systems. These transformers are crucial for applications where the power source converts DC to AC or vice versa, such as in renewable energy systems, industrial motor drives, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
Here are some key details about inverter duty transformers:
- Construction: Inverter duty transformers are typically constructed with materials and winding configurations that can withstand the unique challenges posed by inverter operation. This often includes using materials with high temperature ratings for insulation, such as Nomex or Mylar, and employing techniques like vacuum impregnation to enhance thermal and mechanical stability.
- Harmonics Mitigation: Inverter-based power sources can generate harmonics, which are undesirable and can cause issues such as overheating and voltage distortion. Inverter duty transformers are designed to mitigate these harmonics, often through specialized winding configurations or the use of harmonic filters.
- High Overload Capacity: Inverter duty transformers are built to handle the high overload conditions that can occur in inverter-driven systems. They are often designed to withstand overloads of 150% or more for short durations without significant loss of performance or damage.
- Low Impedance: Transformers used in inverter applications typically have lower impedance compared to standard transformers. This helps to maintain voltage stability and reduce voltage drops, especially during high current and transient conditions common in inverter-driven systems.
- Shielding and Isolation: Inverter duty transformers may include additional shielding to protect sensitive electronics from electromagnetic interference (EMI) generated by the inverter. They also provide electrical isolation between the input and output circuits, ensuring safety and preventing ground loop issues.
- Customization: Inverter duty transformers are often custom-designed to meet the specific requirements of the application, including voltage ratings, frequency compatibility, and physical size constraints.
- Cooling: Efficient cooling is essential for inverter duty transformers, as they are often subjected to higher operating temperatures due to the nature of inverter operation. Cooling methods may include natural convection, forced air cooling, or liquid cooling, depending on the application requirements.
- Compliance: Inverter duty transformers may need to meet specific industry standards and regulations, such as IEEE, NEMA, UL, or IEC standards, depending on the region and application.
Overall, inverter duty transformers play a critical role in ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of inverter-based power systems across various industrial, commercial, and renewable energy applications.