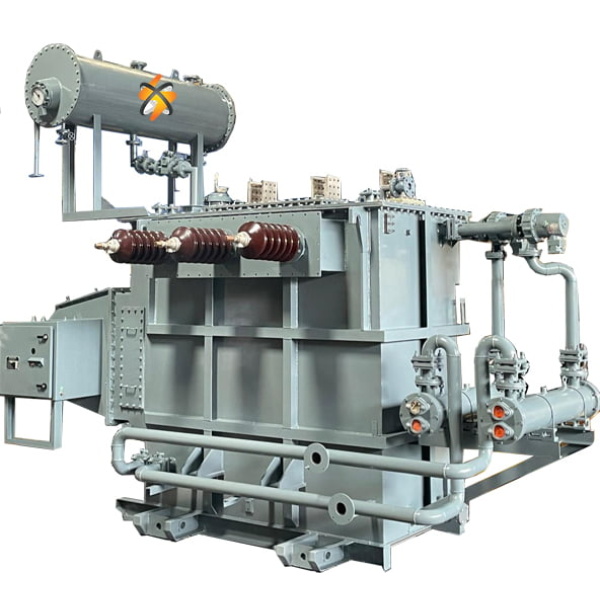
Description
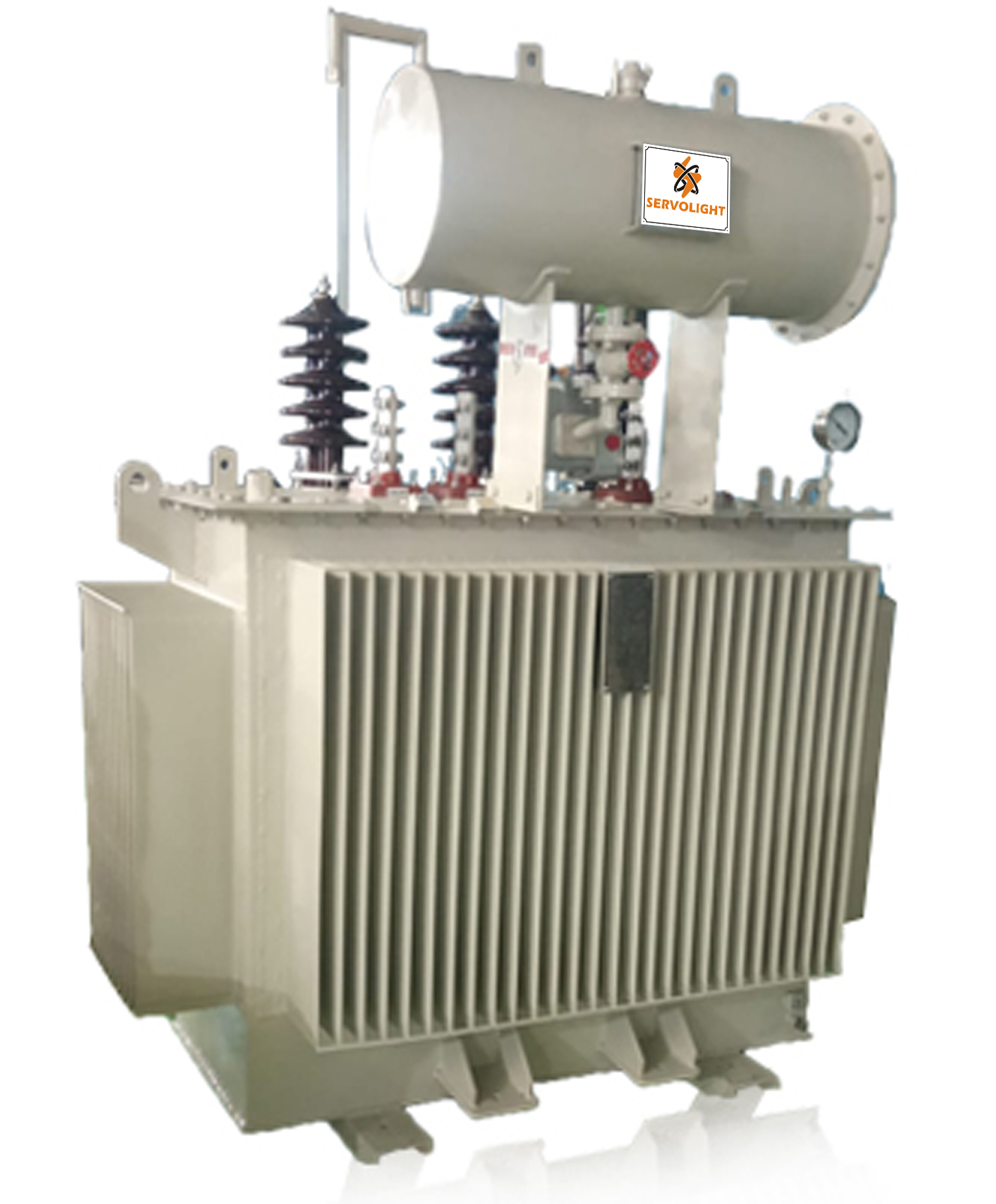
The distribution transformer is a vital component in the electrical grid system, responsible for the final stage of voltage transformation before electricity reaches consumers.
PURPOSE: Distribution transformers serve the purpose of stepping down high-voltage electricity from transmission lines to lower, safer voltages suitable for use in homes, businesses, and other establishments.
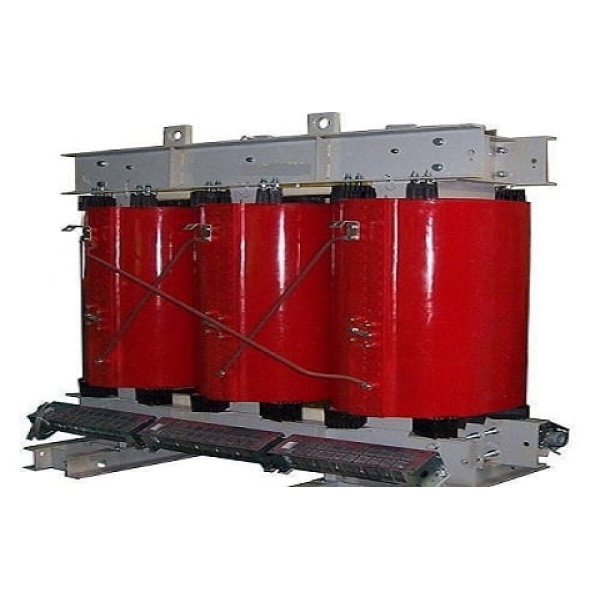
COMPONENTS: These transformers typically consist of a core made of laminated steel sheets, primary and secondary windings, and insulation materials. The core provides a low reluctance path for the magnetic flux generated by the windings
VOLTAGE TRANSFORMATION: Distribution transformers are designed to convert high-voltage electricity (ranging from thousands to hundreds of thousands of volts) down to lower voltages (typically 110V or 220V for residential use).
COOLING SYSTEM: To prevent overheating during operation, distribution transformers are equipped with cooling systems. These may include oil-immersed systems, where the core and windings are submerged in transformer oil, or dry-type systems, where air is used for cooling
EFFICIENCY: Modern distribution transformers are designed for high efficiency to minimize energy loss during the transformation process. Efficiency is crucial for reducing electricity waste and ensuring reliable power distribution.
RANGE:
- UPTO 20 MVA
- Voltage class: 1.1kv,2.2kv, 3.3kv, 6.6kv, 6.9kv,11kv, 12.74kv
13.2kv,15kv, 22kv, 25kv, 33kv, 34.5kv,66kv, 69kv and ++
- Low Voltage class: 380v,400v, 415v, 433v, 440v +++
- Tap changer: OLTC, OLTC
- Cooling: ONAN
USE CASE:
Residential Areas: Distribution transformers are commonly found in residential neighborhoods to supply electricity to homes, apartments, and other dwellings. They reduce the voltage from the main distribution lines to levels suitable for household appliances and lighting.
Commercial Buildings: Distribution transformers are installed in commercial establishments such as offices, shops, malls, and restaurants to power lighting, HVAC systems, computers, and other equipment. Industrial Facilities: Industrial plants and factories require distribution transformers to power machinery, equipment, and lighting systems. These transformers often handle higher loads and voltages compared to residential and commercial applications.
Rural Areas: Distribution transformers are essential for providing electricity to rural and remote areas where power is distributed over long distances. They play a crucial role in rural electrification projects, enabling access to electricity for agricultural activities, small businesses, and households.
Urban Infrastructure: Distribution transformers are installed in urban infrastructure such as streetlights, traffic signals, and public transportation systems. They step down voltage levels for these applications, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
Educational Institutions: Schools, colleges, and universities utilize distribution transformers to power classrooms, laboratories, administrative buildings, and other facilities.
Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals, clinics, and medical centres rely on distribution transformers to ensure uninterrupted power supply for critical medical equipment, lighting, and HVAC systems.